Removal of abdominal fluid is of value in evaluating patients with ascites of new onset or unknown etiology, and provides symptomatic relief in patients with known disease or in the setting of a decompensating clinical state. Abdominal paracentesis is a simple procedure that may be performed rapidly and with a minimum of equipment.
Indications
1.New onset ascites or ascites of unknown origin
2.Patients with ascites of known etiology who may have a decompensation clinical state as indicated by fever, painful abdominal distention, peritoneal irritation, hypotension, encephalopathy or sepsis
3.Suspected malignant ascites
4.Peritoneal dialysis patients with fever, abdominal pain or other signs of sepsis (usually the paracentesis fluid may be removed directly from the patient's dialysis catheter)
Contraindications
1.Uncorrected bleeding diathesis
2.Previous abdominal surgeries with suspected adhesions
3.Severe bowel distention
4.Abdominal wall cellulitis at the proposed site of puncture
Materials
1.Universal precautions materials
2.1-liter vacuum bottles
3.Blood collection tubing, or a secondary IV tubing set
4.18 gauge needle
5.Skin prep solution
6.Sterile draping
7.1% or 2% lidocaine with epinephrine for local anesthesia
8.5 cc syringe with 25 gauge needle for anesthesia infiltration
If available, a bedside ultrasound machine is an asset.
Preprocedure patient education
1.Obtain informed consent
2.Inform the patient of potential complications (infection, hypotension) and their treatment
3.Explain the major steps of the procedure
Procedure
1.Obtain relevant patient history, and perform a physical exam to document and localize ascitic fluid.
2.If ultrasound machine is available, scan patient to localize fluid collections, and perform the procedure under real-time ultrasound guidance.
3.Place patient in supine position, with head elevated 20-300. Select and mark a position on the abdominal wall for puncture (Figure 1)
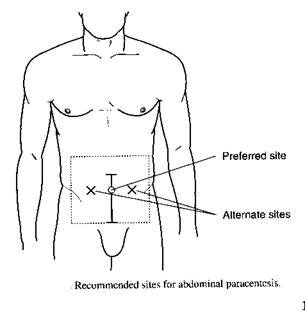
Figure 1.
4.Don sterile gown, gloves, and mask
5.Use skin prep solution to cleanse skin over the proposed puncture site, and drape to define a sterile field
6.Anesthetize the skin over the proposed puncture site with the lidocaine drawn up in the 5 cc syringe with the attached 25 gauge needle. Anesthetize down to the peritoneum. Aspirate periodically; if ascitic fluid returns, withdraw the needle slightly to re-enter tissue before further anesthetic is infiltrated
7.Attach 18 gauge needle to free end of blood collection tubing or the secondary IV tubing. Leave capped. Close valve tightly on the tubing. Puncture the rubber stopper of the vacuum bottle with the other end of the tubing
8.Insert the 18 gauge needle perpendicularly through the anesthetized abdominal wall, and advance until hub of needle is 5mm-1cm from the skin surface. Open up the tubing clamp. Ascitic fluid should begin to flow into the bottle
9.To change vacuum bottles as they become full, close the clamp on the tubing. Then, remove needle of collection tubing from the full bottle, and re-insert into empty bottle. Reopen clamp to start fluid flowing again
10.When paracentesis is done, simply remove needle from abdominal wall. Place a small pressure dressing on puncture site. Have patient remain supine for 2-4 hours
| Complication |
Prevention |
Management |
| Fluid does not flow with opening of clamp |
Check position of insertion and depth of insertion by U/S, or clinical exam |
Adjust depth of insertion or choose another site as fluid may be loculated |
| Fluid is feculent |
Insert needle into area of known fluid collection |
Withdraw needle and choose another site. Observe clinically over next 24 hours for signs or symptoms of peritonitis |
| Fluid is bloody |
Avoid insertion over veins; usually no preventative step |
Check coagulation time prior to paracentesis; withdraw needle
|
| Hypotension after procedure |
Often no warning; limit paracentesis to maximum of 4-5 liters |
Judicious IV saline bolus, Trendelenberg position, 1-2 units of salt-free albumin after removal of 4-5 liters of fluid
|
Complications, Prevention, and Management
Documentation in the medical record
1.Consent
2.Indications and contraindications for procedure
3.Procedure, including prep, anesthetic, needle size, amount of fluid drawn off, character of fluid
4.Any complications or “none”
5.Who was notified of any complication (family, attending MD)
Items for evaluation of person learning this procedure
1.Anatomy of the abdominal wall, locations of bowel in relation to fluid
2.Mechanism of fluid production; etiologies of ascites
3.Indications and contraindications of this procedure
4.Use of sterile procedure and Universal Precautions
5.Interaction between MD, patient, and family
6.Technical ability
7.Appropriate documentation
8.Understanding of potential complications and their correction